What is a Proxy server?
Posted
Proxy: The authority to represent someone else, especially in voting. A person authorized to act on behalf of another.
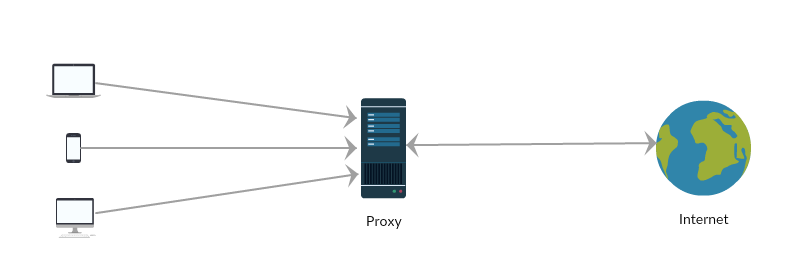
A proxy server in a computer network, is setup as a gateway to the internet (or any other servers) for network clients. In such a setup, the proxy server acts as an intermediary between local network clients and internet. A client connects to the proxy server with a request to resource on internet and proxy server evaluates the request and replies from its cache (if caching is the purpose for implementing a proxy) or forwards to the actual server.
What are some very common types?
- Web proxy: This is the most common application of a proxy server, as mentioned above, it responds to local network clients requests by accessing resources from its cache or from remote web servers. The two fold benefits of such a setup are: cached responses are quicker than getting data from internet and secondly, internet bandwidth is saved. Some examples of such proxy software are: Squid, Nginx, HAProxy, etc.
- Transparent proxy: It intercepts communication at the network layer, without any need of client configuration. In such a setup, clients are hardly aware of a proxy’s existence and it performs some gateway/router functions as well. Transparent proxies, do not modify request or response beyond the requirement of proxy authentication and identification. They are used by organizations to enforce content restriction and caching, maybe more.
- DNS proxy: Caches DNS records locally, looks up for DNS queries in network and forwards to Internet DNS when not in cache.
- Reverse proxy: As it is named, its setup is just the opposite of a proxy, it receives requests from the internet and forwards to internal servers. These are generally used as load balancers and can also cache static content of the servers behind such a proxy. Nginx & HAProxy are widely used for this purpose.
Uses
- Content-filtering: Web proxies provide network administrators enormous control over the content, which is allowed in either direction (incoming and outgoing).
- Encrypted data filtering: Web filtering proxies cannot peep into HTTPS traffic as intercepting into it, will tamper the chain-of-trust (SSL/TLS). Some advanced proxies can (in essence) host a man in the middle attack and own the root certificate allowed by the client. Fiddler is one such software, which can intercept HTTPS traffic on a local computer. There are other sophisticated software, which perform the same job on a network level.
- Circumvent filtering and censorship: If a server employs IP-based geolocation to restrict content to certain countries, it can still be accessed via a proxy hosted in the white-listed country. The client opens a connection with such a proxy and the server sees the request to be originating from an allowed country’s IP and all are happy!
- Performance improvement: A caching proxy speeds response time, when requested resource is found in the cache.
- Security: A proxy can shield internal network of an organization and can be combined with network firewall.